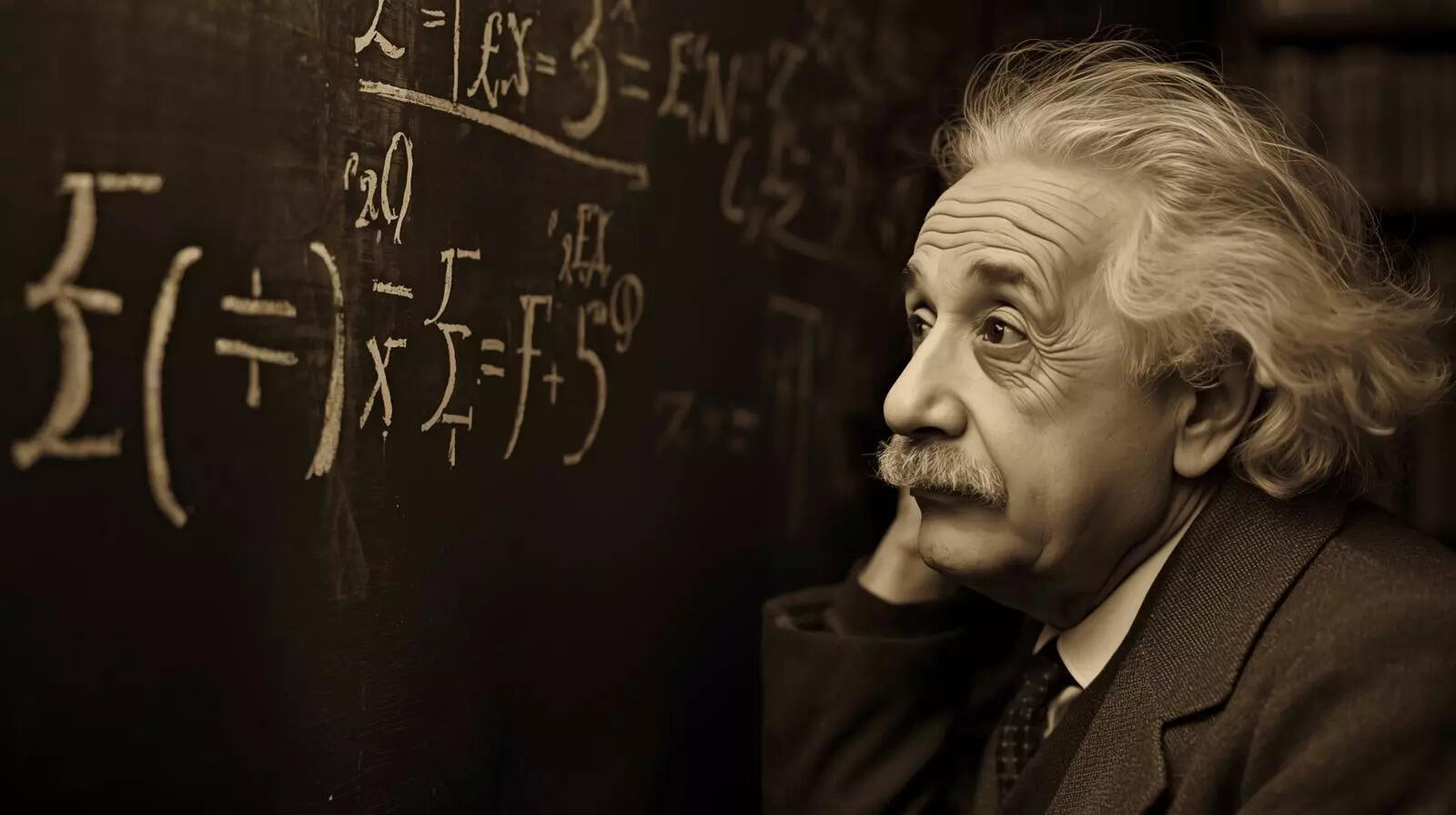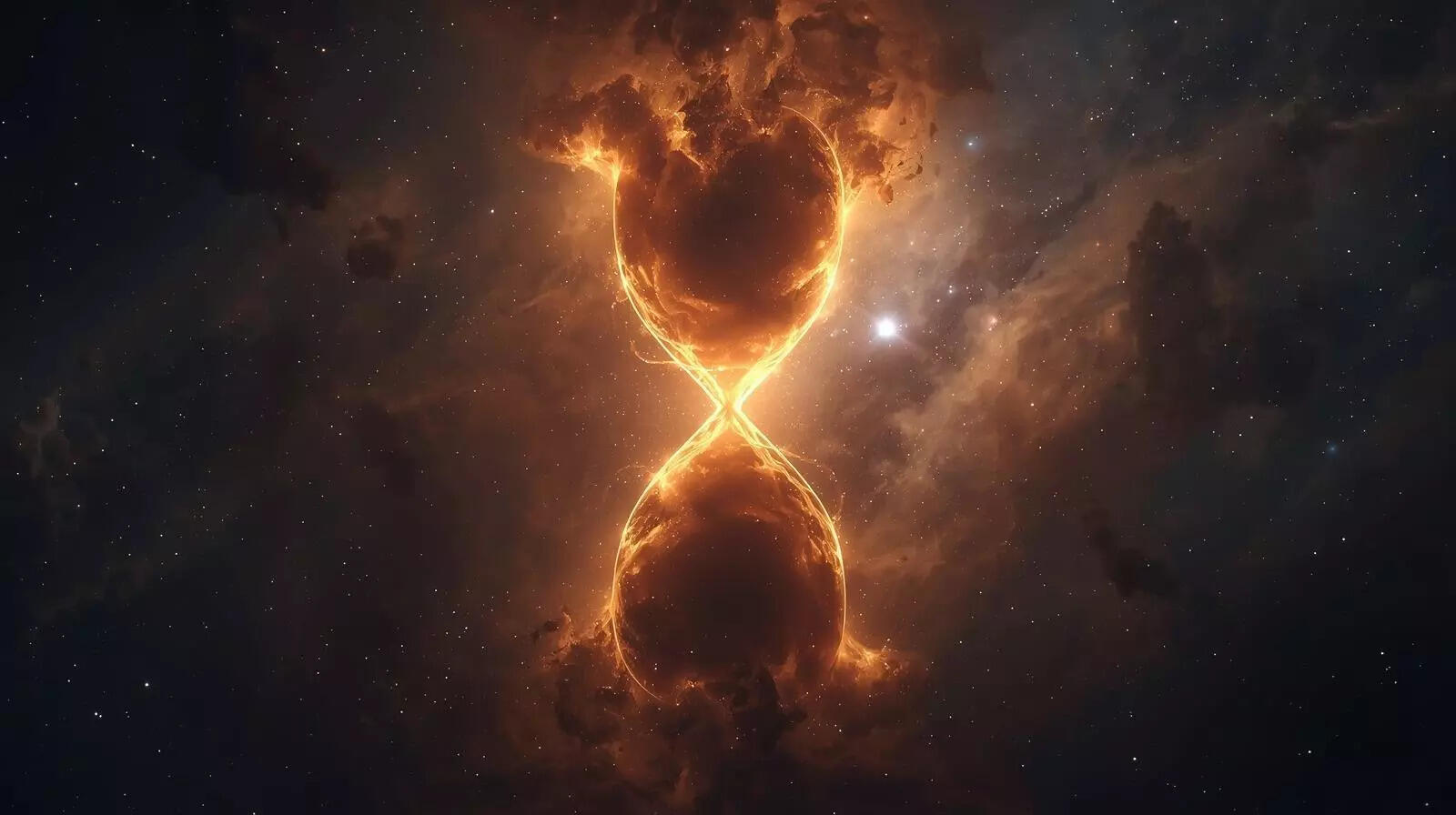✗ Close categories
 Addiction
Addiction
 Apple
Apple
 Apps & Smartphones
Apps & Smartphones
 Arts
Arts
 Asia News
Asia News
 Bollywood
Bollywood
 Books
Books
 Business
Business
 Cars
Cars
 Celebrity
Celebrity
 China
China
 Cinema, Theater & TV
Cinema, Theater & TV
 Coronavirus
Coronavirus
 Culture
Culture
 Digital
Digital
 Ebola
Ebola
 Economy
Economy
 Education
Education
 Electronics
Electronics
 Entertainment
Entertainment
 Environment
Environment
 Europe
Europe
 Fashion
Fashion
 Finance
Finance
 Food
Food
 Funny videos
Funny videos
 Gadgets
Gadgets
 Games
Games
 General News
General News
 Health
Health
 Hollywood
Hollywood
 International Crime
International Crime
 Jobs
Jobs
 Leisure
Leisure
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
 Middle East
Middle East
 Military
Military
 Mindfulness
Mindfulness
 Movies
Movies
 Music
Music
 Nature
Nature
 News videos
News videos
 NewsPhoto
NewsPhoto
 Nightlife
Nightlife
 Olympics
Olympics
 Organized Crime
Organized Crime
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Politics
Politics
 Psychology
Psychology
 Recipes
Recipes
 Religious
Religious
 Sci-Tech
Sci-Tech
 Science
Science
 Sex & Relationships
Sex & Relationships
 Showbizz
Showbizz
 Social media
Social media
 South Asia
South Asia
 Sports
Sports
 Technology
Technology
 Television
Television
 Title
Title
 Traffic
Traffic
 Travel
Travel
 Trending UK
Trending UK
 UK News
UK News
 Weather
Weather
 World News
World News
✗ Close categories
✗ Close categories
✗ Close categories
 American football
American football
 Archery
Archery
 Athletics and triathlon
Athletics and triathlon
 Badminton
Badminton
 Bandy
Bandy
 Baseball and softball
Baseball and softball
 Basketball
Basketball
 Billiards and snooker
Billiards and snooker
 Boxing
Boxing
 Chess
Chess
 Cricket
Cricket
 Cycling
Cycling
 Equestrian sports
Equestrian sports
 Field hockey
Field hockey
 Floorball
Floorball
 Football
Football
 Formula 1
Formula 1
 Gilli-danda
Gilli-danda
 Goa
Goa
 Golf
Golf
 Gymnastics
Gymnastics
 Handball
Handball
 Hockey
Hockey
 Ice hockey
Ice hockey
 Indian Martial Arts
Indian Martial Arts
 Jalikattu
Jalikattu
 Kabaddi
Kabaddi
 Kancha
Kancha
 Karate
Karate
 Kayaking
Kayaking
 Kho-kho
Kho-kho
 Kite-flying
Kite-flying
 Korfball
Korfball
 Lacrosse
Lacrosse
 Motorsports
Motorsports
 Netball
Netball
 Polo
Polo
 Rock climbing
Rock climbing
 Rugby
Rugby
 Sepak takraw
Sepak takraw
 Seval Sandai
Seval Sandai
 Table tennis
Table tennis
 Taekwondo
Taekwondo
 Tennis
Tennis
 Throwball
Throwball
 Traditional and regional sports
Traditional and regional sports
 Volleyball
Volleyball
 Weightlifting and powerlifting
Weightlifting and powerlifting
 Winter sports
Winter sports
 Wrestling
Wrestling
✗ Close categories
✗ Close categories
✗ Close categories
 Agartala
Agartala
 Agra
Agra
 Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
 Ajitgarh
Ajitgarh
 Ajmer
Ajmer
 Alappuzha
Alappuzha
 Aligarh
Aligarh
 Allahabad
Allahabad
 Alwar
Alwar
 Ambala Cantt
Ambala Cantt
 Ambarnath
Ambarnath
 Amritsar
Amritsar
 Anand
Anand
 Anantapur
Anantapur
 Angul
Angul
 Ankleshwar
Ankleshwar
 Aurangabad
Aurangabad
 Baddi
Baddi
 Badlapur
Badlapur
 Bangalore
Bangalore
 Barddhaman
Barddhaman
 Bareilly
Bareilly
 Barnala
Barnala
 Bathinda
Bathinda
 Belgaum
Belgaum
 Bellary
Bellary
 Bharuch
Bharuch
 Bhavnagar
Bhavnagar
 Bhilai
Bhilai
 Bhimavaram
Bhimavaram
 Bhiwandi
Bhiwandi
 Bhopal
Bhopal
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar
 Bhuj
Bhuj
 Bijapur
Bijapur
 Bikaner
Bikaner
 Bilaspur
Bilaspur
 Boisar
Boisar
 Bokaro Steel City
Bokaro Steel City
 Brahmapur
Brahmapur
 Chandigarh
Chandigarh
 Chengannur
Chengannur
 Chennai
Chennai
 Chittoor
Chittoor
 Coimbatore
Coimbatore
 Cuttack
Cuttack
 Dehradun
Dehradun
 Dhanbad
Dhanbad
 Dharamsala
Dharamsala
 Dharwad
Dharwad
 Dhule
Dhule
 Dibrugarh
Dibrugarh
 Dindigul
Dindigul
 Dombivli
Dombivli
 Durgapur
Durgapur
 Eluru
Eluru
 English Bazar
English Bazar
 Ernakulam
Ernakulam
 Erode
Erode
 Faridabad
Faridabad
 Ferozepur
Ferozepur
 Gandhidham
Gandhidham
 Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar
 Ghaziabad
Ghaziabad
 Girinagar
Girinagar
 Gorakhpur
Gorakhpur
 Greater Noida
Greater Noida
 Gulbarga
Gulbarga
 Guntur
Guntur
 Gurgaon
Gurgaon
 Guwahati
Guwahati
 Gwalior
Gwalior
 Haldwani
Haldwani
 Haridwar
Haridwar
 Hisar
Hisar
 Hoshiarpur
Hoshiarpur
 Hospet
Hospet
 Hosur
Hosur
 Howrah
Howrah
 Hubballi
Hubballi
 Hyderabad
Hyderabad
 Imphal
Imphal
 Indore
Indore
 Jabalpur
Jabalpur
 Jaipur
Jaipur
 Jalandhar
Jalandhar
 Jalgaon
Jalgaon
 Jammu
Jammu
 Jamnagar
Jamnagar
 Jamshedpur
Jamshedpur
 Jhansi
Jhansi
 Jharsuguda
Jharsuguda
 Jodhpur
Jodhpur
 Kakinada
Kakinada
 Kakkanad
Kakkanad
 Kalyan
Kalyan
 Kangra
Kangra
 Kannur
Kannur
 Kanpur
Kanpur
 Karaikkudi
Karaikkudi
 Karimnagar
Karimnagar
 Karnal
Karnal
 Karur
Karur
 Khammam
Khammam
 Kharagpur
Kharagpur
 Kochi
Kochi
 Kolhapur
Kolhapur
 Kolkata
Kolkata
 Kollam
Kollam
 Korba
Korba
 Kota
Kota
 Kottayam
Kottayam
 Kozhikode
Kozhikode
 Kurnool
Kurnool
 Kurukshetra
Kurukshetra
 Latur
Latur
 Lucknow
Lucknow
 Ludhiana
Ludhiana
 Madurai
Madurai
 Mangalore
Mangalore
 Manipal
Manipal
 Margao
Margao
 Mathura
Mathura
 Mavelikara
Mavelikara
 Meerut
Meerut
 Mehsana
Mehsana
 Mira Bhayandar
Mira Bhayandar
 Moradabad
Moradabad
 Mullana
Mullana
 Mumbai
Mumbai
 Mysore
Mysore
 Nadiad
Nadiad
 Nagercoil
Nagercoil
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Namakkal
Namakkal
 Nanded
Nanded
 Nashik
Nashik
 Navi Mumbai
Navi Mumbai
 Navsari
Navsari
 Nellore
Nellore
 New Delhi
New Delhi
 Nizamabad
Nizamabad
 Noida
Noida
 Ongole
Ongole
 Palakkad
Palakkad
 Panaji
Panaji
 Panipat
Panipat
 Pathanamthitta
Pathanamthitta
 Patiala
Patiala
 Patna
Patna
 Pilani
Pilani
 Pimpri Chinchwad
Pimpri Chinchwad
 Puducherry
Puducherry
 Pune
Pune
 Purnia
Purnia
 Raigarh
Raigarh
 Raipur
Raipur
 Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry
 Rajkot
Rajkot
 Ranchi
Ranchi
 Raysan
Raysan
 Rishikesh
Rishikesh
 Rohtak
Rohtak
 Roorkee
Roorkee
 Rourkela
Rourkela
 Rudrapur
Rudrapur
 Sagar
Sagar
 Salem
Salem
 Samastipur
Samastipur
 Sambalpur
Sambalpur
 Sangrur
Sangrur
 Satara
Satara
 Satna
Satna
 Secunderabad
Secunderabad
 Shillong
Shillong
 Shimla
Shimla
 Shimoga
Shimoga
 Silchar
Silchar
 Siliguri
Siliguri
 Sivakasi
Sivakasi
 Solapur
Solapur
 Sonipat
Sonipat
 Srinagar
Srinagar
 Surat
Surat
 Tezpur
Tezpur
 Thane
Thane
 Thanjavur
Thanjavur
 Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram
 Thoothukudi
Thoothukudi
 Thrissur
Thrissur
 Tiruchirappalli
Tiruchirappalli
 Tirunelveli
Tirunelveli
 Tirupati
Tirupati
 Tiruppur
Tiruppur
 Udaipur
Udaipur
 Udupi
Udupi
 Ulhasnagar
Ulhasnagar
 Unnao
Unnao
 Vadodara
Vadodara
 Valsad
Valsad
 Vapi
Vapi
 Varanasi
Varanasi
 Vasai
Vasai
 Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama
 Vellore
Vellore
 Vijayawada
Vijayawada
 Virar
Virar
 Virudhunagar
Virudhunagar
 Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Warangal
Warangal
 Yamuna Nagar
Yamuna Nagar
✗ Close categories
✗ Close categories
-
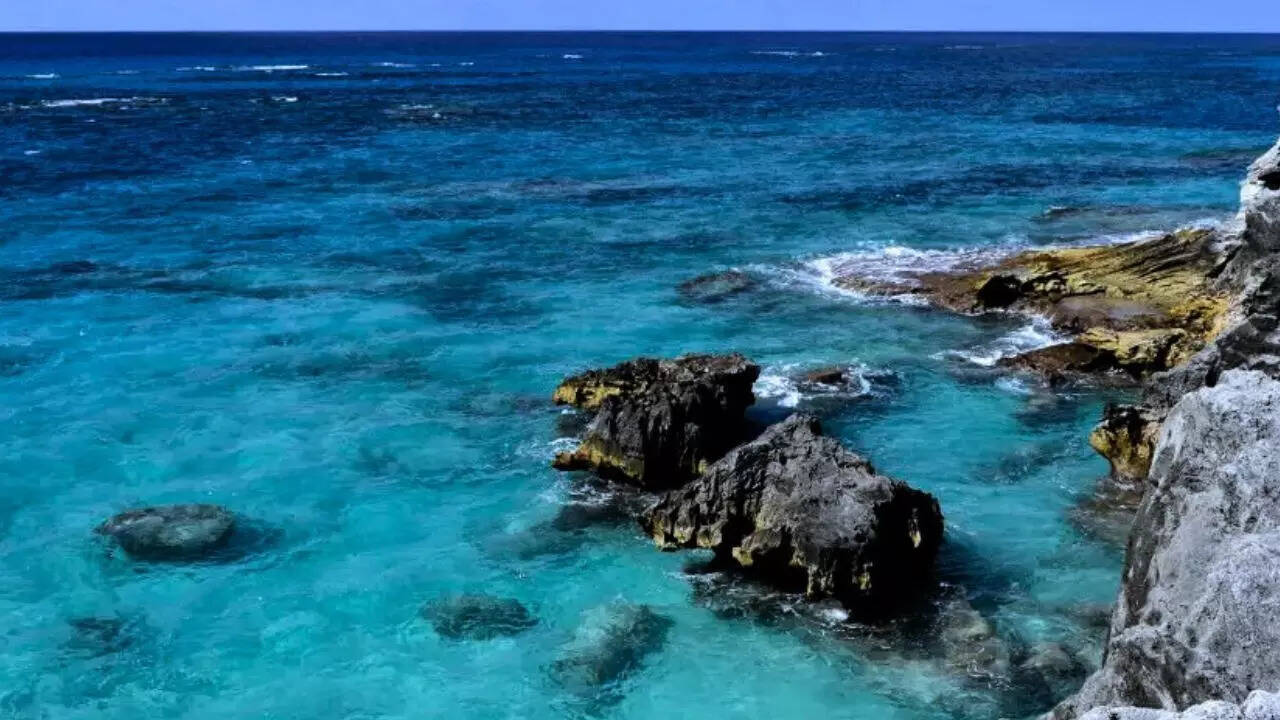
Strange new discovery in the Bermuda Triangle stuns scientists: 20-km-thick rock layer found beneath surface
Scientists have discovered an unusually thick rock layer, approximately 20 kilometers deep, beneath the Bermuda Triangle. This geological feature, unlike any previously documented, may explain the region's elevated seafloor despite a lack of recent volcanic activity. The discovery challenges existing models of oceanic crust formation and evolution. -
Meet 3I-ATLAS, The Ancient Cosmic Voyager: Could This Interstellar Comet Be Older Than The Sun?
Interstellar comet 3I-ATLAS is a rare cosmic visitor that may be older than our Sun, offering scientists a unique glimpse into the early Milky Way. Its ancient origins and unusual composition could help unlock secrets about the formation of stars and planets. -
Scientists say a space explosion 13,000 years ago may have changed life on Earth
A new study suggests a comet exploded in the sky 13,000 years ago. This event caused Earth's sudden cooling, known as the Younger Dryas. Large animals like mammoths vanished. The Clovis people disappeared. Evidence includes melted glass and shocked quartz found in ancient soil. This theory explains the abrupt changes without a ground impact crater. -
Can Human Body Sense Death Before It Happens? Brain's Sixth Sense Ability Will Leave You Shocked
Some scientific studies from brain research suggest that near death, there may be brief bursts of electrical activity in the brain and changes in neurochemicals. -
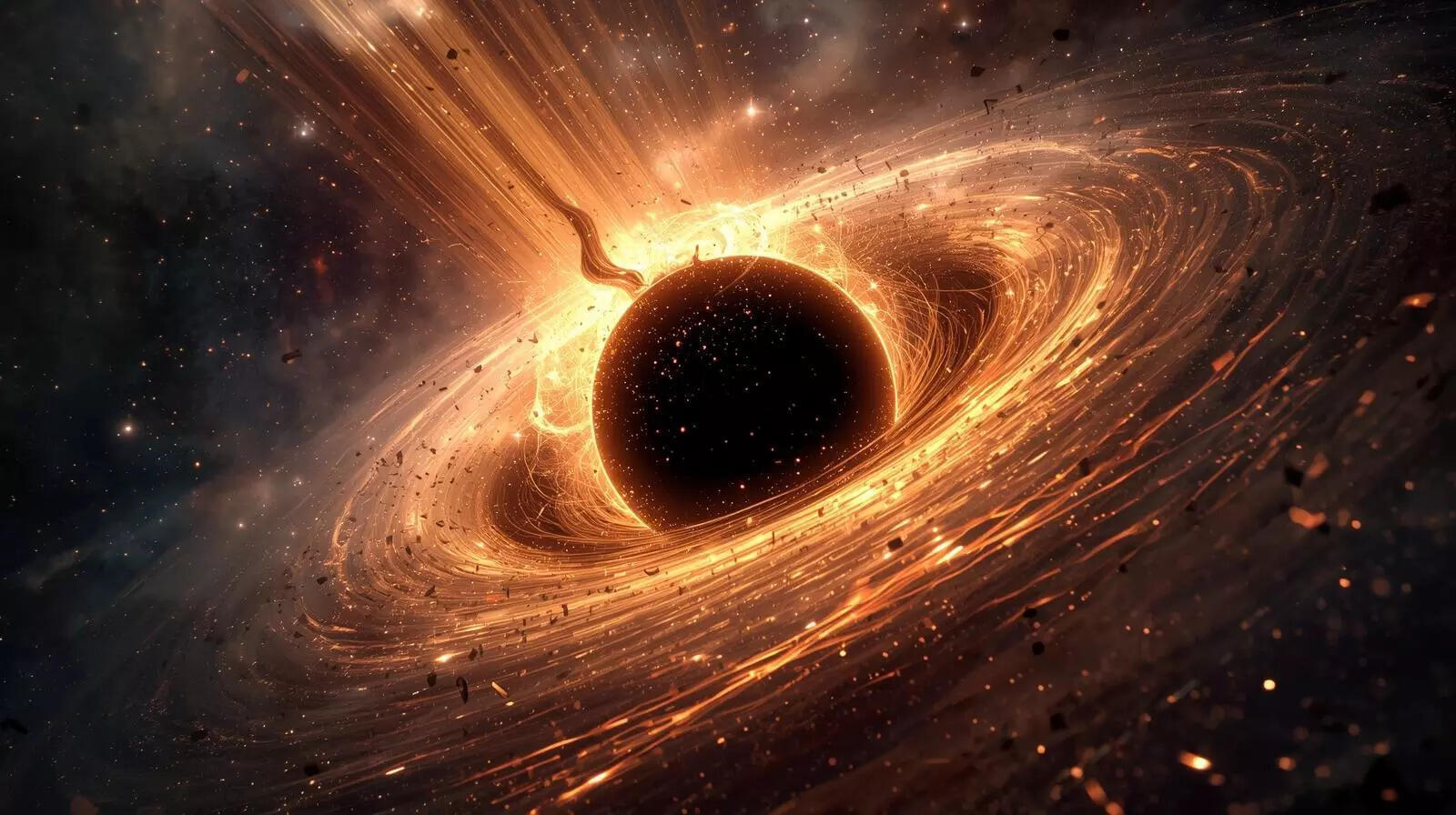
Black holes are twisting the universe: New discovery shows Einstein was right
Astronomers have observed a distant star being torn apart by a supermassive black hole, revealing a surprising wobble in the resulting disc and jets. This phenomenon, matching Einstein's century-old prediction of 'frame dragging,' provides compelling evidence that spinning black holes twist spacetime itself, influencing cosmic events and refining our understanding of galactic evolution. -
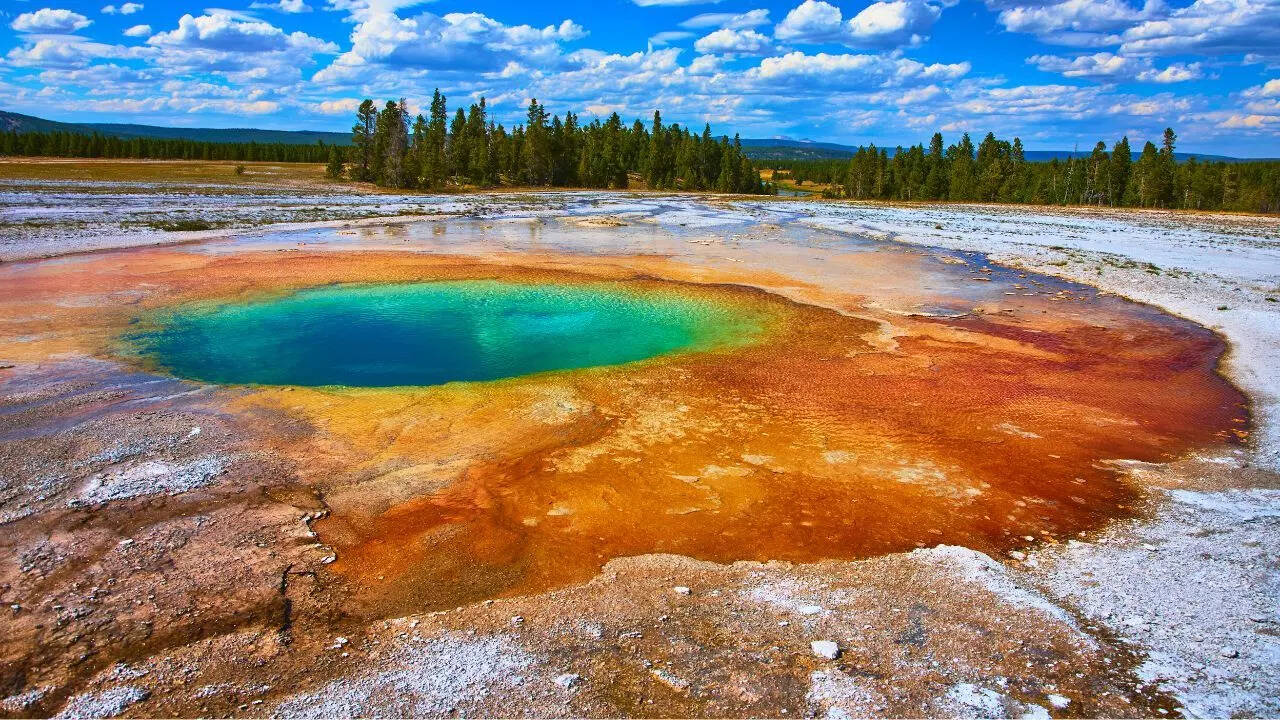
What lies beneath Yellowstone in Wyoming is far more complex than a supervolcano
Yellowstone's volcanic past reveals a dynamic system of repeated caldera-forming eruptions and smaller lava flows, with magma reservoirs assembling and erupting on geologically brief timescales.Beneath the surface, a crystal-rich mush stores melt, capable of rapid renewal.This ancient activity also records Earth's magnetic history, offering crucial global chronological data. -
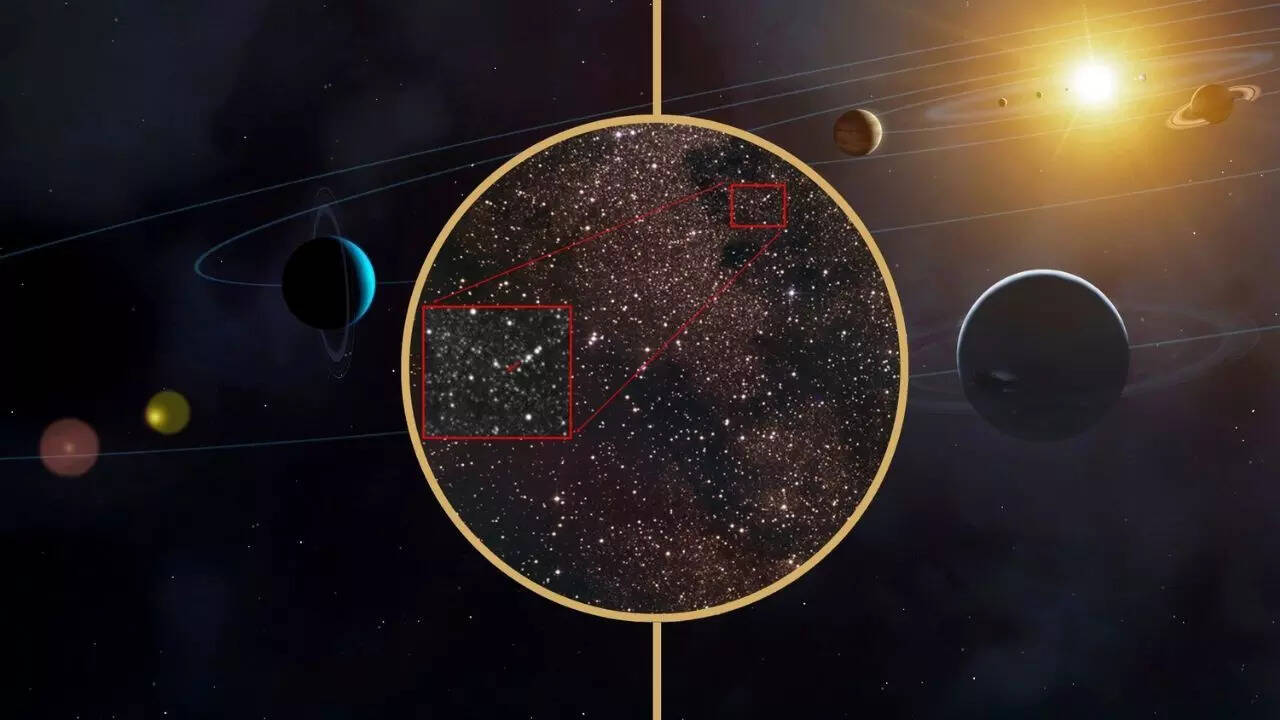
Is interstellar object 3I/ATLAS older than our Sun? Here’s what it might reveal about the origins and observations
Astronomers have discovered 3I/ATLAS, a fast-moving interstellar object detected in mid-2025. Researchers believe this ancient comet, potentially 8-14 billion years old, originated from the Milky Way's earliest era, predating our Sun. Its unique chemical composition, including iron and nickel, further supports its alien origins, offering a rare glimpse into material forged around ancient stars. -
What really happens when astronauts cry in space
In space, tears don't fall due to the absence of gravity. Instead, surface tension causes them to cling to the eye, creating a physical sensation and potential vision blur. Astronauts manage these tears with absorbent cloths, a process vital for understanding human physiology in microgravity and for future long-duration missions. -
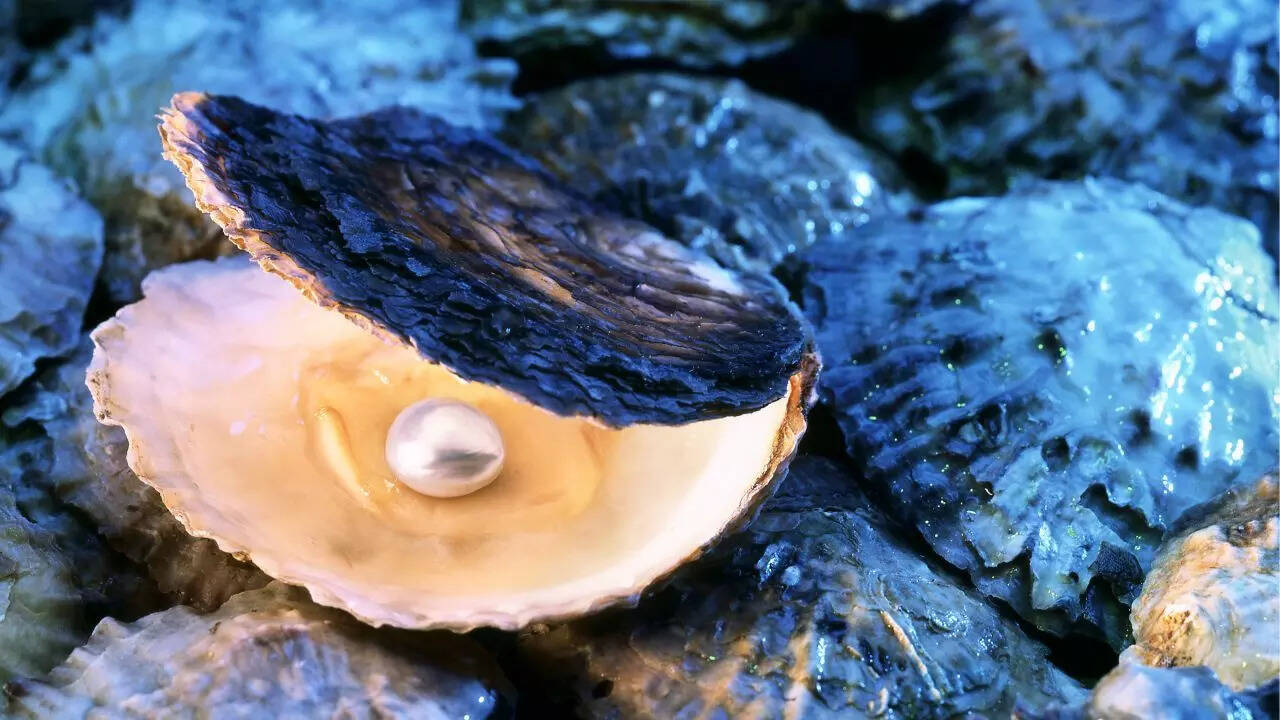
How oysters turn a tiny irritant into a pearl: What really goes on inside the shell
Pearls begin as irritants within oysters, which respond by slowly covering the foreign object with layers of nacre. This controlled biological process, influenced by environmental factors and diet, transforms discomfort into a stable, beautiful structure. Cultured pearls follow the same natural oyster response, with quality determined by nacre thickness and lustre, not just size. -
Einstein was fascinated by this math problem because it had no solution
Albert Einstein encountered a curious math puzzle involving an old car on a hill. The problem, seemingly simple, highlighted how intuition can be misleading. It demonstrated that faster speeds do not always compensate for slower ones and that averages can obscure critical limitations. This thought experiment, shared through correspondence, underscored the importance of careful examination even of basic questions. -
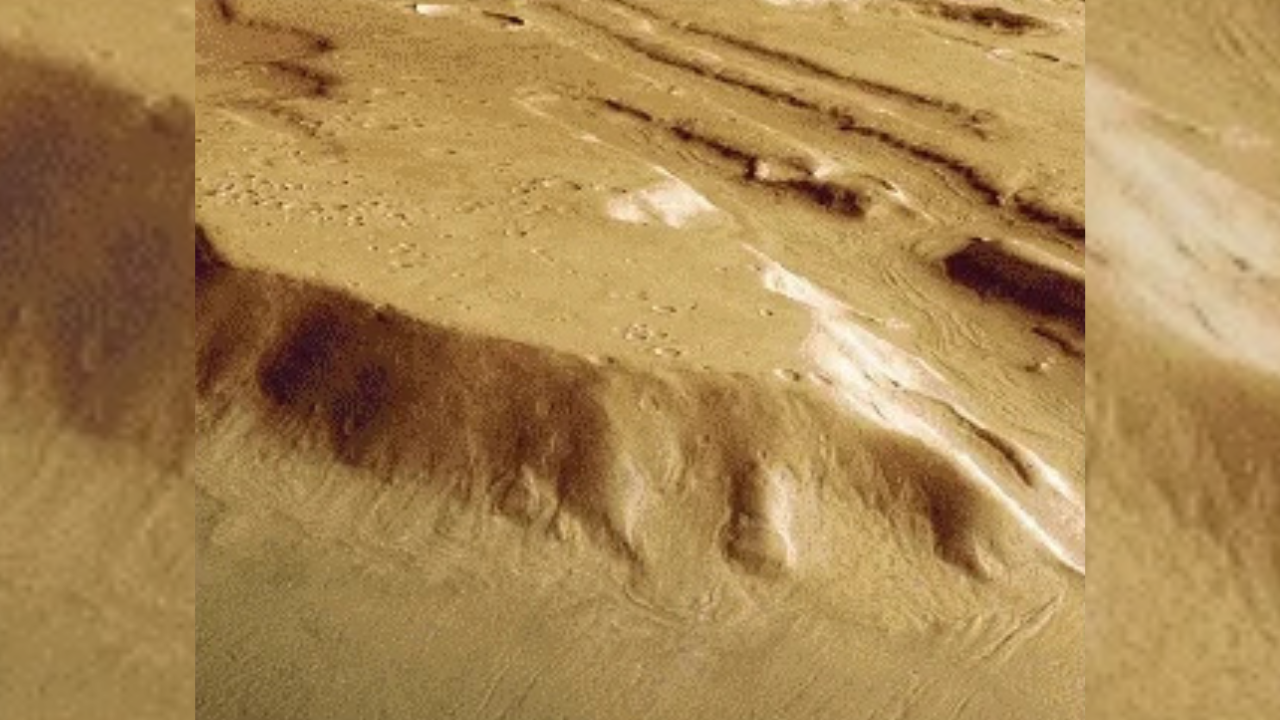
Fresh images of Mars show signs of relatively recent ice age
Evidence of a past Martian ice age has been revealed in Coloe Fossae, where long, shallow grooves suggest ice once flowed across the landscape. These features, formed by slow-moving mixtures of ice and rock, indicate glaciers spread into mid-latitudes, offering a glimpse into Mars's icy history as recently as half a million years ago. -
Astronomers identify a planet that travels through the Milky Way without orbiting the Sun
Astronomers have directly observed a free-floating planet, comparable in mass to Earth, roaming the Milky Way. Discovered via gravitational microlensing due to its brief light curve, this rogue world is not bound to any star. Its motion suggests ejection from a planetary system, hinting at a potentially vast population of such solitary planets. -
AI is guzzling water and power. Here’s what we can do about it
AI's rapid rise hides a massive thirst for water and energy. Training complex models like ChatGPT demands immense power, leading to significant water consumption for cooling data centers. Experts propose solutions like efficient cooling, smaller models, and renewable energy to mitigate AI's growing environmental footprint. -
Scientists trying to build computers that think like brains using mushrooms
Scientists are exploring fungi, specifically mushrooms, to create more efficient and adaptable computers. Unlike rigid silicon machines, fungal networks like mycelium exhibit learning-like behavior by adjusting signal pathways. This biological approach offers a potentially cheaper and more resilient alternative to current complex and costly neuromorphic hardware, hinting at a novel direction for future computing. -
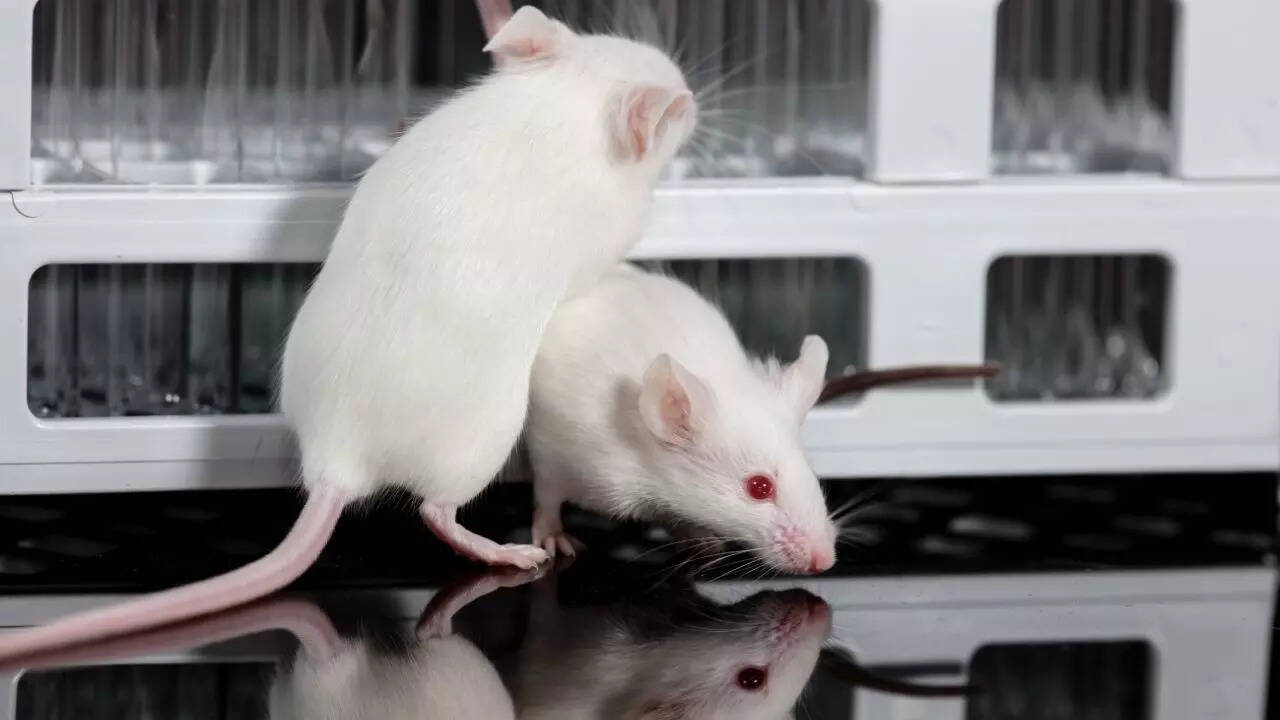
Why do scientists use mice for experiments and how do they mirror human biology
Mice are indispensable in biomedical research due to their genetic and anatomical similarities to humans, short lifespans, and rapid reproduction. They have been crucial in developing treatments for cancers, vaccines for pandemics like COVID-19, and understanding neurodegenerative disorders. Ethical guidelines ensure responsible use, with advancements like CRISPR enhancing accuracy and reducing animal numbers. -
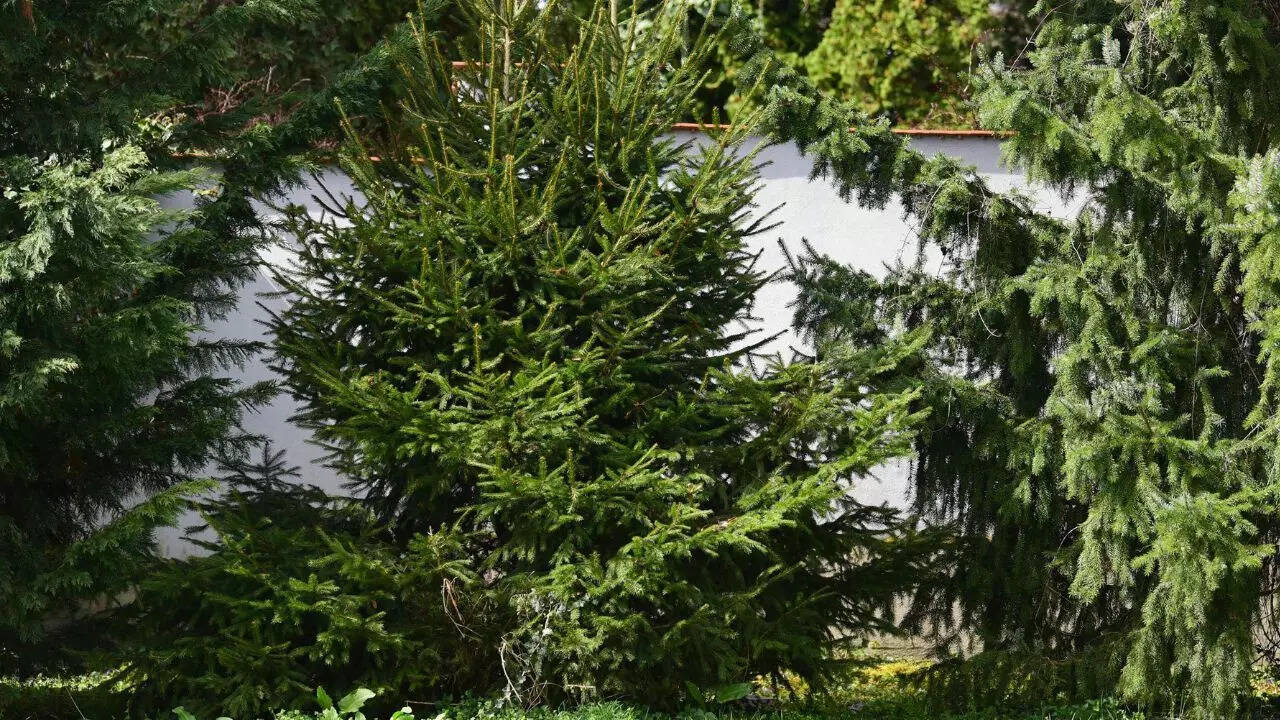
The tree that grows gold: Scientists explain how hidden microbes inside living plants are turning dissolved ions into solid metal
Scientists are baffled by solid gold particles found in Norway spruce needles. Previously thought impossible, this discovery reveals a partnership between trees and specific bacteria. These microbes, not the trees, are believed to convert dissolved gold ions into solid nanoparticles, a process crucial for understanding mineral deposits and potentially cleaning polluted environments. -
January is the best month to see Jupiter: Here's when and where to look up
Jupiter will be exceptionally bright and large in the night sky this January, peaking around January 10, 2026, during Earth's opposition. This celestial event, occurring roughly every 13 months, makes the planet easily visible to the naked eye, even offering glimpses of its moons with binoculars. -
Neil deGrasse Tyson calls Moon-landing denial a ‘disconnect from reality’ on Logan Paul’s podcast
Astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson confronts Moon-landing denial during a podcast appearance, rejecting scepticism with physics, scale and evidence. From lunar rocks and Saturn V maths to the implausibility of a 400,000-person conspiracy, he explains why Apollo isn’t belief-based history. The argument matters because mistrust survives not through gaps in proof, but misunderstanding, and modern spaceflight puts the debate in perspective. -
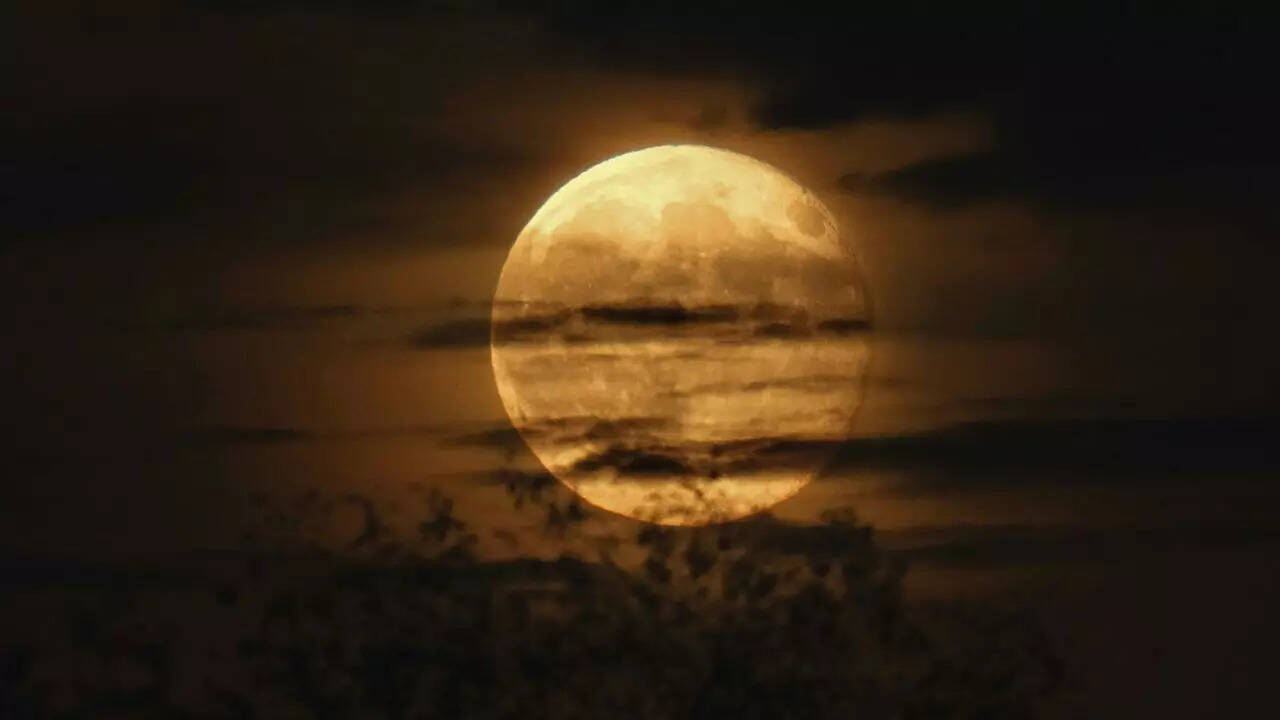
Wolf Moon 2026: Date, Time, And How To Watch India’s First Full Moon Of The Year
The first Supermoon of 2026 is set to light up Indian skies, appearing bigger and brighter than usual. Here’s everything you need to know about its date, time, and the best way to watch this rare celestial event. -
What happens if the Moon disappears
Earth's oceans would experience significantly smaller tides without the Moon. Marine life dependent on tidal motion would face drastic changes. Nocturnal predators and prey behavior would shift dramatically. Earth's axial tilt would become unstable, leading to extreme seasonal variations over long periods. Human activities, from coastal industries to agriculture, would be profoundly impacted. -
What would happen if the Sun exploded suddenly
Our Sun will not explode like other stars. Instead, it will slowly expand into a red giant, consuming inner planets. This process will take billions of years. After this phase, the Sun will shrink to a dense white dwarf. The solar system will become cold and dark. This future event is extremely far away, offering humanity ample time. -
10 myths about lightning and why you should not believe them
Many common beliefs about lightning are myths.These ideas often stem from simple observations and are passed down without question.Modern technology allows us to track lightning and compare it with these beliefs.Studies reveal significant differences between what people think and what actually happens.Understanding these facts can help people stay safer during storms. -
What would happen to the world if lithium became scarce
Our reliance on lithium, powering everyday devices, faces a hidden fragility.Despite abundant reserves, access is concentrated, and recycling is minimal, leading to constant mining.While alternatives like sodium-ion batteries and solid-state technology are emerging, their widespread adoption is slow, suggesting a future of careful management and reduced lithium use per device rather than complete absence. -
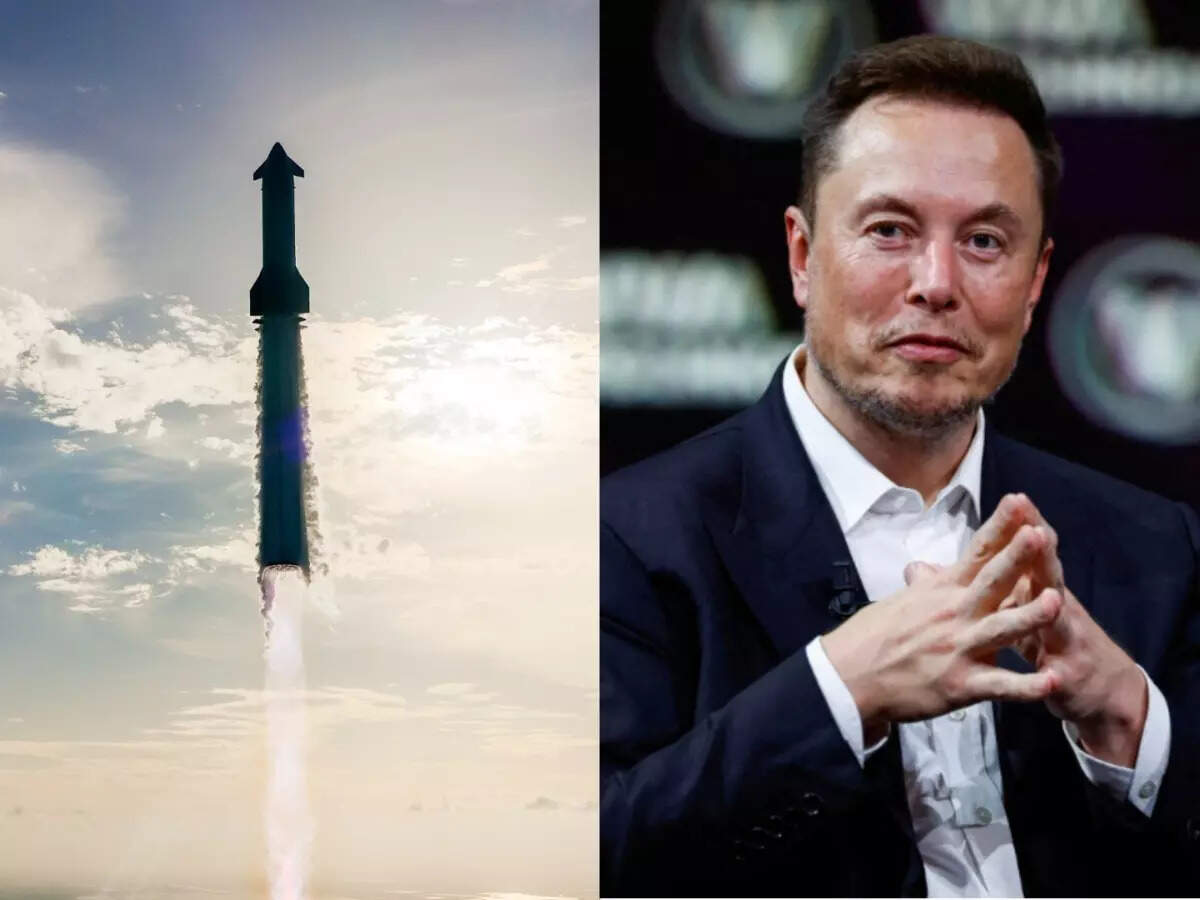
Starlink is quietly moving its satellites closer to Earth and there’s a reason
SpaceX plans to lower Starlink satellites to a safer orbit in 2026. This move aims to reduce collision risks and space debris. Satellites will burn up faster at the end of their life. This decision follows a recent satellite failure. SpaceX is the world's largest satellite operator. The change focuses on safety and sustainability in low Earth orbit. -
Astronauts experience New Year 2026 celebrations 16 times in space: Here’s why and how time works differently in orbit
Astronauts aboard the International Space Station experienced New Year 2026 sixteen times, witnessing the transition to a new year with each of their 90-minute orbits.This unique perspective highlights the vast differences in time perception between Earth and space, where daily cycles of daylight and darkness are compressed.Their adherence to Greenwich Mean Time structures life in orbit. -
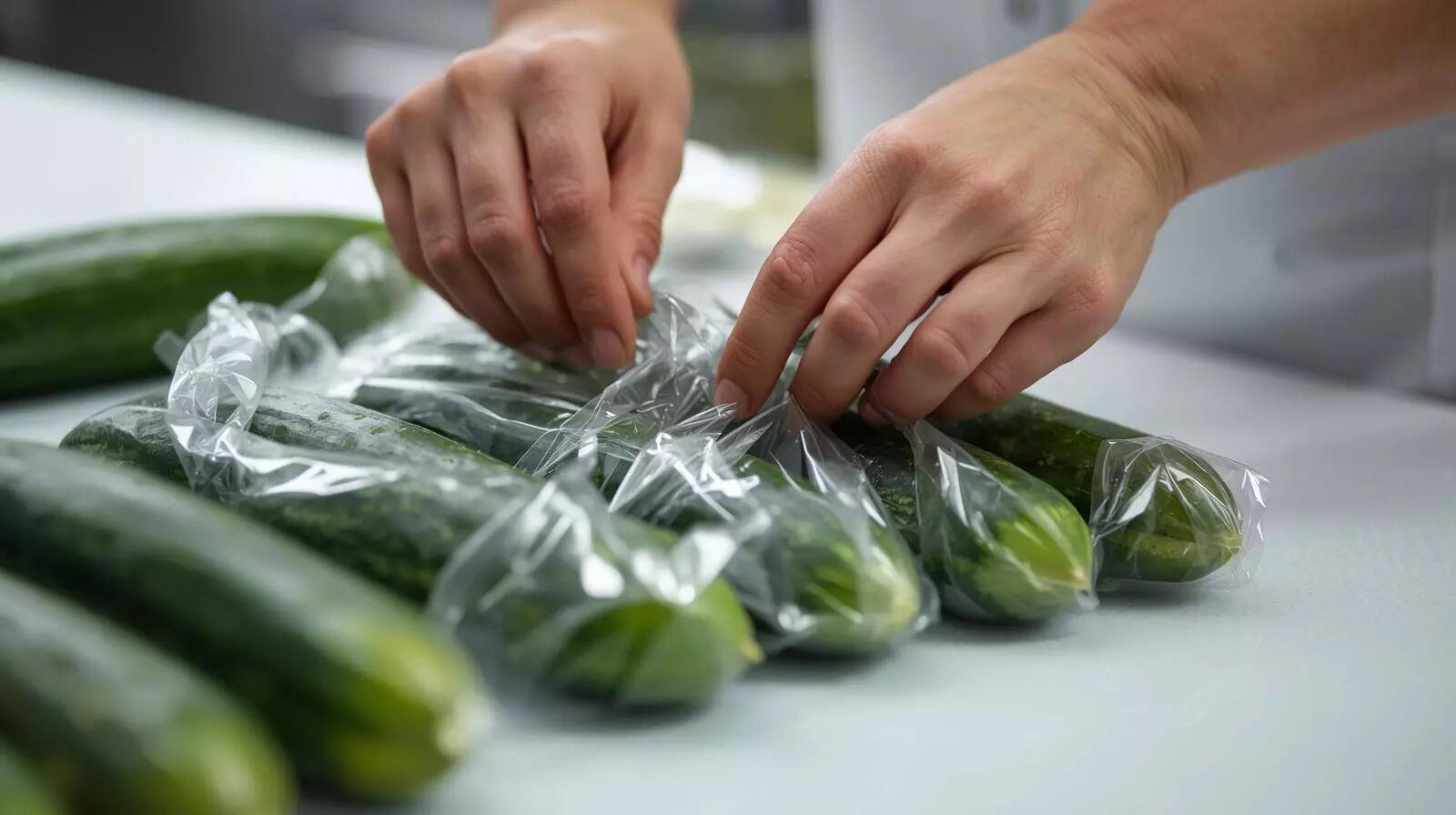
Does wrapping cucumbers in plastic really harm the planet; know the truth
Plastic wrapping on cucumbers is not as bad as it seems. It helps keep cucumbers fresh during long journeys. This reduces food waste, which is a bigger environmental problem than the plastic itself. Growing food uses many resources. Wasting a cucumber wastes all those resources. Plastic wrap protects cucumbers from damage and decay. -
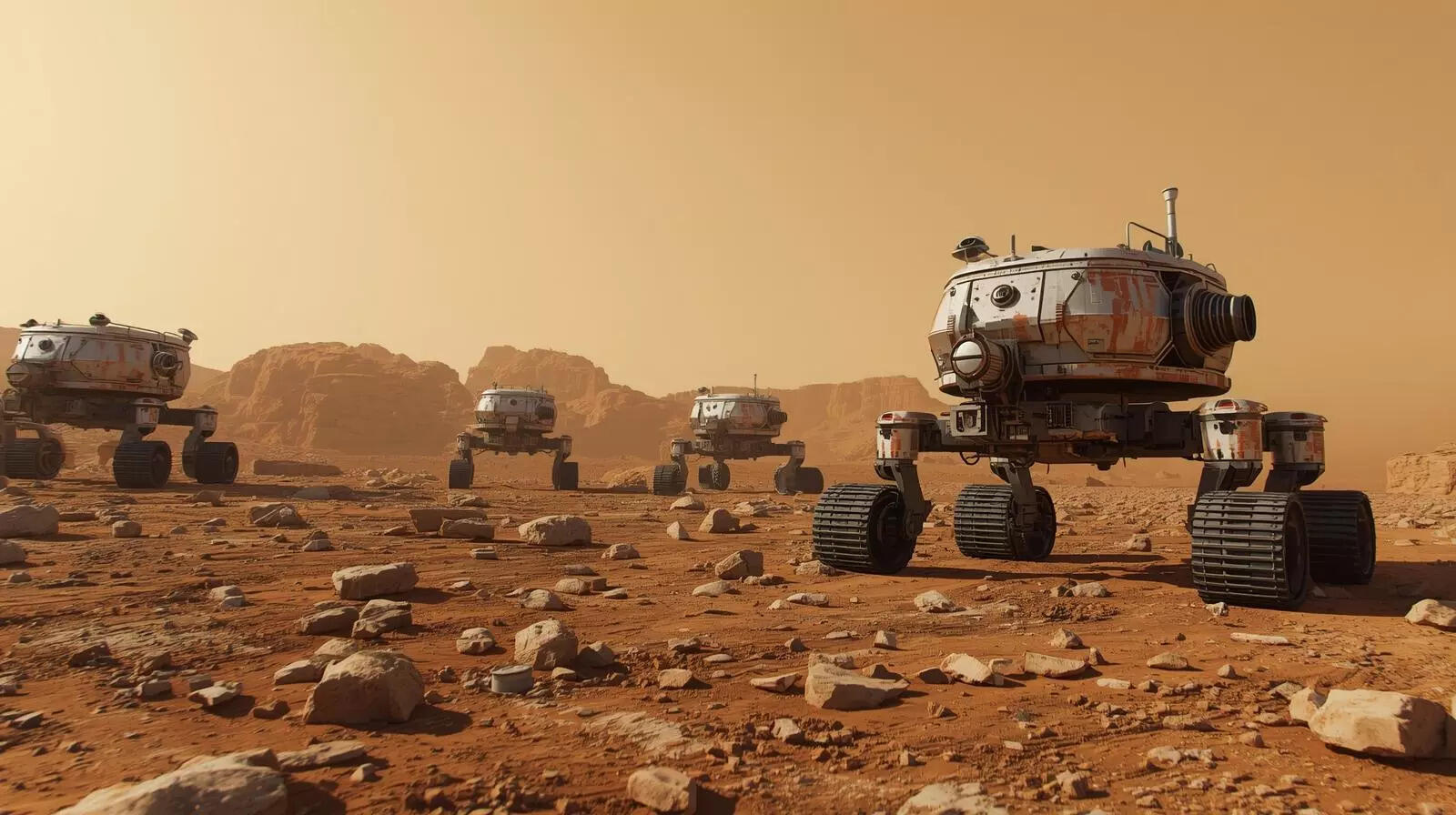
Nasa is using robots to quietly shape the road to Mars
Robots are paving the way for humans on the Moon and Mars. Missions are currently tracking radiation, mapping water, and studying dust. This vital data helps plan safe habitats and routines. Ingenuity-like drones may even find natural radiation shelters. These machines are working patiently, shaping the future of space exploration. -
Cockroaches with tiny backpacks could become the world’s most unexpected spy technology
A German firm is turning cockroaches into spy tools and rescuers. These insects can navigate dangerous areas where machines and people cannot. Equipped with tiny cameras and microphones, they gather intelligence. The technology also holds promise for disaster response, locating survivors in collapsed buildings. This innovation is reshaping defense and surveillance capabilities. -
How a tiny piece of orbital debris exposed a major safety risk in China’s Shenzhou mission
China's Shenzhou-20 mission faced a critical delay when a small crack appeared in the return capsule's window.This damage, caused by fast-moving space debris, threatened the astronauts' safety.An emergency mission launched a replacement spacecraft, ensuring a safe return.The incident underscores the significant risks posed by even microscopic space junk and prompts a review of orbital safety measures. -
Astronomers notice an hourglass like shape while scanning an ordinary galaxy
Astronomers found a giant hourglass shape around a galaxy called ESO 130 G012. This structure is made of radio waves and stretches over 160,000 light-years. It extends far beyond the galaxy's visible stars. Scientists are studying how this enormous outflow formed. It may be from steady star formation or a past black hole event.